Australia: A brief overview
Land and climate
In terms of land area, Australia is approximated to be about 7,692,024 sq.km and is the 6th largest nation in the world. However, population wise, the country has a relatively smaller population. Australia is a nation of many contrasts. For instance, mainland Australia is not only the largest island but it also is the smallest and flattest continent on the planet. The interesting thing about the nation, however, is that about one out of every four Australian was born in another country, or either one or both of their parents was born overseas. Only 2% of the population is made up by indigenous citizens and these are the Torres Strait Islanders and the Aboriginals.
Seasons
The seasons in the temperate zone are described in terms of European seasons applied to the southern hemisphere in the following sequence:
- Summer: December to February
- Autumn: March to May
- Winter: June to August
- Spring: September to November
In the southern capital cities: Sydney, Canberra, Melbourne, Hobart, Adelaide and Perth, defined by the temperate zone, the average temperatures are: Summer minimum 16 and Summer maximum 26 and Winter minimum 6 and Winter maximum 14, all in degrees Celsius.
In the sub-tropic and tropical cities the average minimum temperatures are: Brisbane 16 and Darwin 23 with the average maximums: Brisbane 25 and Darwin 32. In the inland city of Alice Springs, surrounded by desert and grassland, the average minimum is 20 and the average maximum is 32.
Language
English is largely monolingual being the de facto national language.
Universities and Colleges in Australia
There are 43 universities in Australia: 40 public universities, two international universities, and one private university. The Commonwealth Higher Education Support Act 2003 sets out three groups of Australian higher education providers: universities, other self-accrediting higher education institutions, and state and territory accredited higher education institutions.
Tertiary education
Tertiary education includes both higher education (including universities) and vocational education and training (VET).
Australian Qualifications Framework
The Australian education system is distinguished from many other countries by the Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF). The AQF was established in 1995 and is a national policy that covers qualifications from the tertiary education sector (higher education and vocational education and training) in addition to the school-leaving certificate; the Senior Secondary Certificate of Education.
The AQF has 10 levels and links school, vocational and university education qualifications into one national system. This allows you to move easily from one level of study to the next, and from one institution to another, as long as you satisfy student visa requirements. It allows for choice and flexibility in career planning. All qualifications in the AQF help prepare you for both further study and your working life.
If you are studying an AQF qualification, you can be sure that your institution is Government-authorised and nationally accredited, and that your degree or other AQF qualification will be genuine.
The institutions are linked across the country and across the world, which makes it easy to move throughout the education system between courses or institutions and formal agreement and recognition frameworks mean every step of the path will contribute to your future no matter what your study or career goals.
List of Australian Universities
Economy
Australia, a vibrant free-market democracy, has recorded impressive economic progress unmarred by recession for more than 25 years. In addition to abundant natural resources, the economy has benefited from an effective system of government, a well-functioning legal system, and an independent bureaucracy, all of which have facilitated robust entrepreneurial development.
Australia is one of the wealthiest Asia–Pacific nations and has enjoyed more than two decades of economic expansion. It emerged from the 2009 global recession relatively unscathed,
The economy of Australia is one of the largest mixed market economies in the world, with a GDP of AUD$1.62 trillion as of 2015. Australia is the 19th-largest importer and 19th-largest exporter.
The Australian economy is dominated by its service sector, comprising 68% of GDP. The mining sector represents 7% of GDP; including services to mining, the total value of the mining industry in 2009-10 was 8.4% of GDP. Economic growth is largely dependent on the mining sector and agricultural sector (12% of GDP) with the products to be exported mainly to the East Asian market.
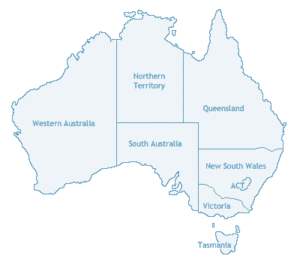
States and territories of Australia
Australia (officially known as the Commonwealth of Australia) is a federation of six states, together with ten federal territories. The Australian mainland consists of five of the six federated states and three of the federal territories (the "internal" territories).
Canberra, in the Australian Capital Territory, is Australia's capital city.
Australian Capital Territory
New South Wales
Northern Territory
Queensland
South Australia
Tasmania
Victoria
Western Australia
Map of Australia by States


Recent Comments